

CSR reporting is an increasingly popular way for businesses to display their sustainability performance and build credibility. A compelling CSR report can strengthen corporate relationships between employees, stakeholders, and consumers. In this guide, we’ll explore the ins and outs of CSR reporting by covering the following topics:
Keep in mind there is no “perfect” CSR report to rely on. Instead, your CSR report should encapsulate your company’s values and show tangible evidence of its commitment to responsibly steward its resources and influence.

Corporate social responsibility also known as CSR or corporate citizenship describes a company’s efforts to improve society in some way.
These efforts fall into several categories such as volunteering, donating cash or in-kind goods or services, or changing operational systems to benefit environmental or social justice-related causes. Although it is not a mandated practice in the U.S., CSR positively impacts companies, employees, and society as a whole and can function as a meaningful differentiator for companies that participate.
A CSR report, also known as an extra-financial report or an ESG (environmental social governance) report, is a document published by a company (usually annually) to provide evidence of its CSR efforts and results.
Although there is not a common set of reporting standards in the U.S., typically a CSR report captures at least one of the four categories: environmental, ethical, philanthropic, or economic impact.
Sustainability reporting falls under ESG reporting which stands for environmental, social, and governance reporting which acts as a quantifiable measurement of a company’s social impact outcome.
Currently, U.S.-based companies are not legally required to provide an ESG report. However, all companies are encouraged to produce ESG reports to provide company insights that pave the way for a more sustainable future.
The United States Security and Exchange Commission (SEC) only requires companies to report on information that may be material to investors, including ESG-related risks. This policy could change soon as the SEC proposed in May 2022 certain “amendments to rules and reporting forms to promote consistent, comparable, and reliable information for investors concerning funds’ and advisers’ incorporation of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors.”
That said, delivering a CSR report should be about more than just maintaining potential legal compliance. Instead, it’s about demonstrating your commitment to making the world a better place through responsible stewardship of resources.
Aside from the positive societal and environmental impact it accounts for, CSR reporting is important because it communicates and provides evidence for your company’s values. To break it down further, comprehensive CSR reporting accomplishes the following objectives:
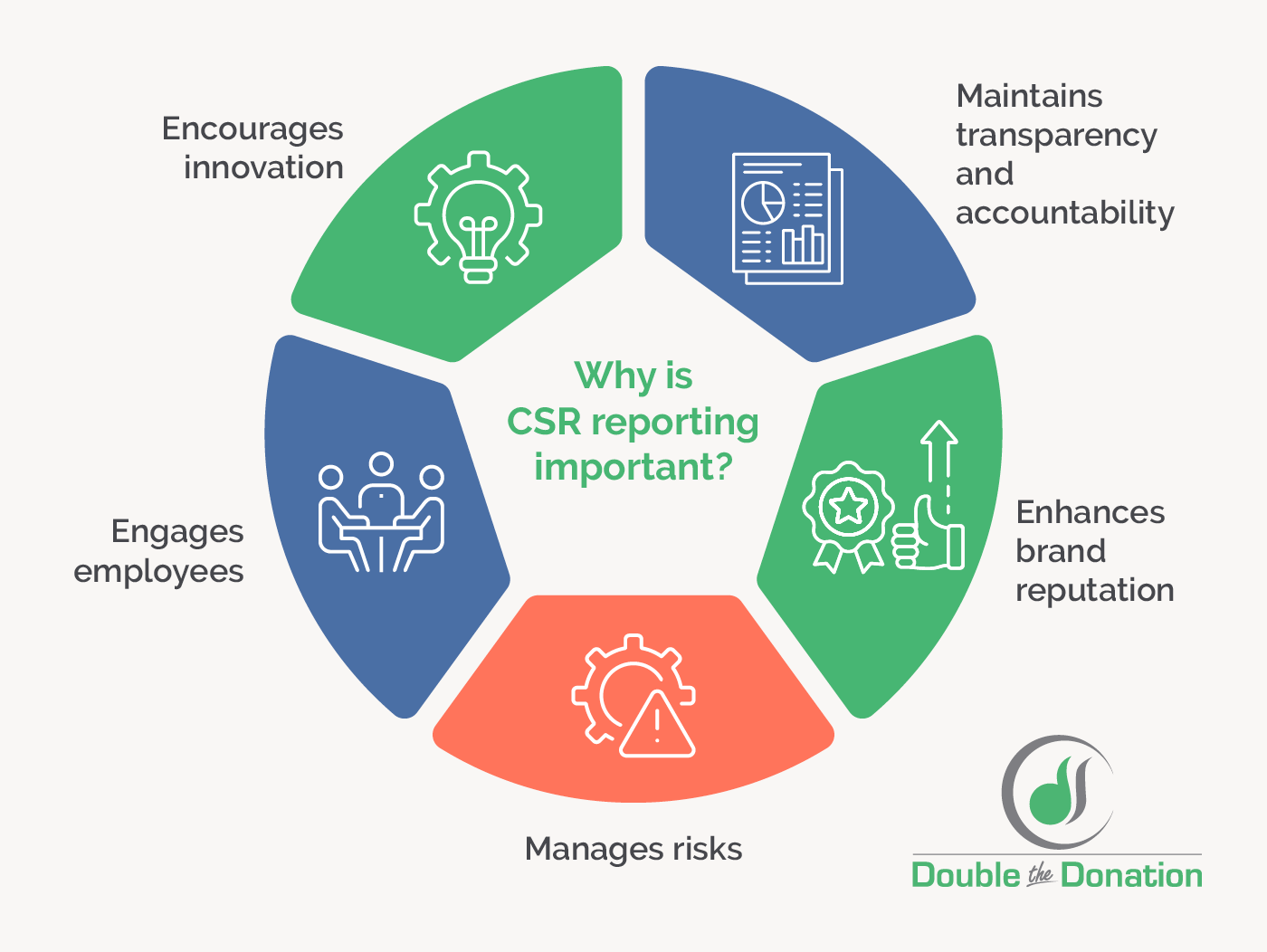
For all these reasons, CSR reporting should be a staple at every socially responsible organization as doing so will ensure a company’s internal aims align with its actions. And, if the United States decides to follow the European Union’s lead and enforce distinct reporting standards, companies well-versed in CSR reporting will already have a leg up.
When writing any report, knowing your audience and why they’d be interested in reading it is helpful. In the case of a CSR report, the document will target both internal and external parties. Let’s take a look at each below.

Investors are interested in CSR reports because they want to assess your company’s long-term sustainability and ethical practices. Specifically, they evaluate ESG risks and the strategies your company has in place to mitigate them.
Investors are also concerned with your company’s financial performance, so a data-backed CSR report that details associated cost savings and market share increase can be a valuable asset for attracting this group.
Customers read CSR reports to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their values. For example, 50% of survey respondents even reported conducting online research to see how a business reacts to social issues before making a buying decision.
Remember a customer’s perspective when finalizing your report. For example, a local company may opt to highlight its local community involvement through programs or partnerships. This also translates to choosing engaging imagery and using customer-friendly language.
Employees read CSR reports to better understand their employer’s values, ethics, and contributions to society to see if their values align. More recently, employees have noted that CSR is a paramount decision-making factor for new employees as 93% believe companies must lead with purpose.
Therefore, your CSR report can also act as a retention and recruitment tool by plan by highlighting your company’s sustainability and social good plans and accomplishments
Because CSR reports can vary in length, subject matter, and style, it can be difficult to know where to start. To help you out, we’ve provided CSR reporting do’s and don’ts for you to compare below:

Now that you know the basics of CSR reporting, you might be wondering, How can I take my report to the next level? To start, you’ll want to review your current CSR programs and data collection methods. Other strategies that can take your CSR strategy above and beyond are listed below:
Comprehensive CSR reporting requires that your company keep track of several programs at once spanning from environmental causes to social and economic initiatives. With a CSR platform, your team can manage these historic and incoming data points with ease.
These software solutions make it simple to ingrain your social, environmental, and philanthropic values into your day-to-day operations. This way, you can prioritize your societal impact without sacrificing focus on your company’s growth and long-term success. Aside from streamlining your workflow, CSR platforms can help you reap several benefits, including:
When shopping for the right CSR software, look for a platform that compliments your existing technology. For example, CSR software with an auto-submission integration can skyrocket your employee matching gift participation by making it easier than ever to submit a matching gift request.
This way, when an employee donates to a nonprofit, they only need to submit their corporate email address, and the software automates the rest of the request submission process.
Check out this brief video to understand how the auto-submission feature fits into your CSR strategy:
As seen in the video, CSR software integration can significantly help boost employee participation and elevate your matching gift programs.
Your data and performance indicators must be contextualized to be useful for the reader. This means you’ll need to explain the importance of each of your initiatives and provide an honest picture of your progress. Here are a few strategies you can use to offer a complete summary:
By adding these strategies to your CSR report, you’ll provide additional clarity to your readers and effectively communicate your sustainability journey. This way, you’ll foster trust and confidence by exploring the full picture of your company’s challenges and successes.
Sometimes it’s helpful to have a few examples to refer to when drafting your CSR report. To help guide your research I’ve handpicked three companies with stellar CSR reports and listed what makes each report worth emulating below:
The Social Metaverse Company, or Meta, “builds technologies that help people connect, find communities, and grow businesses.” They specialize in creating immersive technologies that facilitate new social experiences.
Meta’s 2023 CSR report’s forward-thinking strategy makes it worth considering. The company’s concrete and transparent approach to net zero emissions gives the reader a better understanding of its strategy. Take a look at its carbon emissions breakdown below:

This graph shows Meta’s 2022 carbon footprint and the description of how it has achieved net zero emissions in its global operations.
Additionally, the report goes on to say that reaching net zero emissions is not enough and lays out a plan to decarbonize it’s footprint beyond its offices and data centers. Specifically, to align with the Paris Agreement, Meta has set a goal to reach net zero emissions across its value chain in 2030.
This forward-thinking approach uses historical data to set both achievable and measurable goals as Meta sets out to design with less, incorporate sustainable supply chain principles, and embrace low-carbon technology.
The Campell Soup company is committed to “bringing people together through food they love.” The company’s soups, simple meals, snacks, and beverages are in alignment with its health and well-being goals.
Campell Soup’s homestyle messaging rings through in its 2022 CSR report. The report’s clear branding and engaging visuals remind readers of the company’s purpose. Additionally, the programs Campell Soup supports such as its school nutrition partnerships align with its values:

By providing nutrition education in a variety of school settings to support awareness of and pique interest in nutritious food choices, Campbell Soup affirms its dedication to improving food access and education.
This is just one example of a CSR program that is aligned with Campbell’s Soups values. For more details, check out the full report below.
Intel specializes in providing technology that seeks to improve the life of every person. The company has driven business and society forward with innovation, expertise, and forward-thinking products.
A main thread of the company’s beliefs is interconnectivity which is alive and well within Intel’s CSR report. Multiple letters from company leadership including the CEO and CPO clearly outline the report’s goals.

Additionally, Intel’s emphasis on employee engagement and stakeholder transparency sets it apart. According to the Executive Vice President “Maintaining a strong culture and positive employee relations is paramount as we grow and transform Intel”.
And, Intel’s integrated investor outreach program speaks to its commitment to corporate accountability. By getting the perspective of multiple stakeholders, Intel’s CSR report is an example of effective collaboration. View the report below for more details.
CSR reports are necessary tools to communicate your company’s sustainability and environmental goals. When drafting your report be sure to include accurate and complete data that builds credibility. Consider researching the reports of companies within your sector to get a better understanding of how to structure your report.
We hope you enjoyed this guide to CSR reporting. Check out these resources to continue learning:
https://doublethedonation.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/CSR-Reporting_Feature.jpg 720 1920 Adam Weinger https://doublethedonation.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/logo-dtd.svg Adam Weinger 2024-03-04 19:10:54 2024-03-04 19:10:54 Pursuing Accountability: CSR Reporting Strategies & Examples

A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
Most Popular Terms: